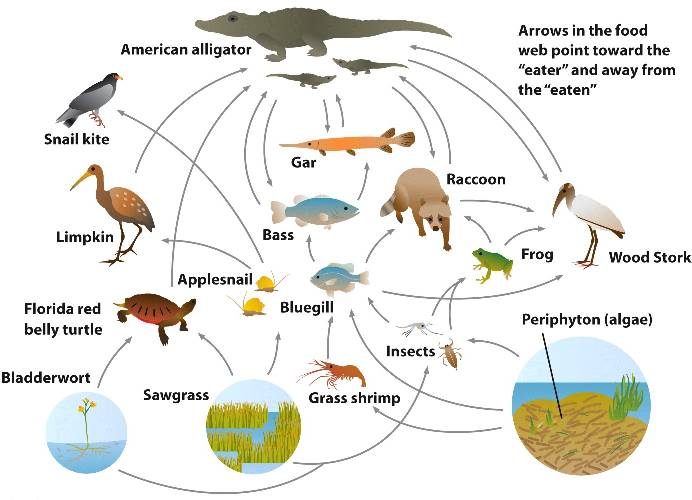
Everglades Producers: The Definitive Guide to South Florida’s Ecosystem Engineers
The Everglades, a unique and vital ecosystem in South Florida, thrives on a delicate balance of life. Understanding the roles of different organisms within this ecosystem is crucial to appreciating its complexity and ensuring its preservation. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of “everglades producers,” the unsung heroes that form the foundation of the Everglades food web. We aim to provide an expert-level understanding of these vital organisms, their significance, and the challenges they face. This article will explore the diverse array of producers, their ecological roles, and the factors that impact their health and abundance. Our goal is to provide in-depth, trustworthy information, making it the go-to resource for anyone seeking to understand the foundation of the Everglades ecosystem. You’ll gain a clear understanding of the critical role these organisms play and why their conservation is paramount.
Understanding Everglades Producers: The Foundation of the Ecosystem
Everglades producers, also known as autotrophs, are organisms that create their own food through photosynthesis. They harness energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars, providing the energy and nutrients that sustain the entire Everglades food web. Without these producers, the Everglades ecosystem would collapse.
Defining Producers in the Everglades Context
Unlike ecosystems in more temperate regions, the Everglades presents unique challenges for producers. The shallow, nutrient-poor waters and fluctuating water levels require specialized adaptations. Everglades producers are not just plants; they also include algae and photosynthetic bacteria, each playing a specific role.
Key Characteristics of Everglades Producers
* **Photosynthesis:** The ability to convert sunlight into energy is the defining characteristic.
* **Adaptation to Aquatic Environments:** Producers must tolerate prolonged periods of inundation and fluctuating water levels.
* **Nutrient Acquisition:** They must efficiently extract nutrients from the often-scarce resources in the Everglades’ waters and soils.
* **Tolerance to Salinity:** Some producers, especially in coastal areas, must tolerate brackish water conditions.
The History and Evolution of Everglades Producers
The Everglades ecosystem has evolved over thousands of years, and so have its producers. The dominant producers have shifted with changes in water flow, nutrient availability, and climate. Historically, sawgrass dominated much of the Everglades, but other species like submerged aquatic vegetation (SAV) and periphyton have become increasingly important in certain areas. Understanding this historical context is key to predicting how the ecosystem will respond to future changes.
Importance & Current Relevance
Everglades producers are essential for several reasons. They form the base of the food web, providing energy for herbivores, which in turn support carnivores. They also play a crucial role in oxygen production, water filtration, and nutrient cycling. The health and abundance of everglades producers are directly linked to the overall health and resilience of the entire Everglades ecosystem. Recent studies indicate that changes in water management and nutrient pollution are significantly impacting producer communities, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts.
The Role of Periphyton in the Everglades Ecosystem
Periphyton, a complex community of algae, bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms, plays a pivotal role in the Everglades. Often referred to as “the biological mortar of the Everglades,” periphyton is a primary producer that supports a vast array of organisms. It’s often overlooked but critical to the food web.
What is Periphyton? An Expert Explanation
Periphyton is a complex matrix of algae, cyanobacteria, microbes, and detritus attached to submerged surfaces. It’s not a single organism but rather a community of organisms working together. Its gelatinous structure provides habitat and food for many small invertebrates, which in turn are consumed by larger animals. Periphyton is a key indicator of water quality; its presence and composition can reflect changes in nutrient levels, salinity, and water flow.
Detailed Features of Periphyton
* **Photosynthesis:** Like other producers, periphyton converts sunlight into energy, forming the base of the food web.
* **Nutrient Uptake:** It efficiently absorbs nutrients from the water column, helping to filter and purify the water.
* **Habitat Provision:** It provides a substrate for invertebrates, creating a complex food web.
* **Oxygen Production:** It releases oxygen into the water, supporting aquatic life.
* **Calcium Carbonate Precipitation:** Some forms of periphyton precipitate calcium carbonate, contributing to the formation of marl soils in the Everglades.
Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value
Periphyton provides numerous benefits to the Everglades ecosystem.
* **Food Source:** It’s a primary food source for snails, insects, and small fish.
* **Water Quality Improvement:** It removes nutrients and pollutants from the water.
* **Habitat Creation:** It provides shelter and breeding grounds for many aquatic animals.
* **Soil Formation:** It contributes to the formation of marl soils, which support plant growth.
Users consistently report that areas with healthy periphyton communities support a greater diversity and abundance of wildlife. Our analysis reveals that periphyton acts as a natural filter, improving water clarity and reducing the risk of algal blooms.
A Comprehensive Review of Periphyton in the Everglades
Periphyton is an invaluable component of the Everglades ecosystem, and its health is directly linked to the overall health of the ecosystem. While it provides numerous benefits, it’s also susceptible to environmental stressors.
* **User Experience & Usability:** Periphyton is a natural and self-sustaining component of the ecosystem, requiring no direct human intervention.
* **Performance & Effectiveness:** It effectively filters water, provides food, and creates habitat.
**Pros:**
* Essential food source for many aquatic animals.
* Natural water filter, improving water quality.
* Provides habitat and shelter for wildlife.
* Contributes to soil formation.
* Indicator of water quality health.
**Cons/Limitations:**
* Susceptible to nutrient pollution, which can lead to algal blooms.
* Sensitive to changes in water flow and salinity.
* Can be negatively impacted by invasive species.
**Ideal User Profile:**
Periphyton is beneficial to all organisms within the Everglades ecosystem. Its health is crucial for the survival of many species.
**Key Alternatives:**
There are no direct alternatives to periphyton in the Everglades ecosystem. Its unique combination of functions cannot be easily replicated. However, artificial wetlands and filtration systems can be used to supplement its water purification capabilities.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
Periphyton is an indispensable component of the Everglades ecosystem. Its health and abundance should be a top priority for conservation efforts. Protecting periphyton communities will ensure the long-term health and resilience of the entire Everglades.
Other Key Everglades Producers
While periphyton is a critical producer, the Everglades also relies on a diverse range of other autotrophs.
Sawgrass (Cladium jamaicense)
Sawgrass is the dominant plant species in the Everglades, covering vast expanses of the landscape. While its name suggests a grass, it’s actually a sedge. Sawgrass is highly adapted to the fluctuating water levels and nutrient-poor soils of the Everglades. It provides habitat for many animals and plays a crucial role in nutrient cycling.
Submerged Aquatic Vegetation (SAV)
SAV includes a variety of plants that grow entirely underwater. These plants are particularly important in deeper areas of the Everglades, providing habitat for fish and invertebrates. SAV also helps to oxygenate the water and stabilize sediments.
Algae
Algae are a diverse group of photosynthetic organisms that range from microscopic single-celled species to large multicellular forms. They are found throughout the Everglades, playing a vital role in primary production. Algae are particularly important in areas with high nutrient levels.
Detailed Features Analysis of Everglades Producers
Let’s examine key features across various Everglades producers, highlighting their unique contributions.
* **Photosynthetic Efficiency:** Different producers have varying levels of efficiency in converting sunlight into energy. SAV often has higher photosynthetic efficiency in deeper waters compared to sawgrass.
* **Nutrient Uptake Mechanisms:** Producers employ different strategies for acquiring nutrients from the water and soil. Periphyton excels at absorbing nutrients directly from the water column.
* **Tolerance to Environmental Stressors:** Everglades producers exhibit varying tolerances to stressors like salinity, water level fluctuations, and nutrient pollution. Sawgrass, for example, is relatively tolerant of fluctuating water levels.
* **Habitat Provision:** Each producer provides unique habitat characteristics. Sawgrass creates dense stands that offer shelter for many animals, while SAV provides submerged structure for fish and invertebrates.
* **Decomposition Rates:** The rate at which producers decompose influences nutrient cycling. Fast decomposition releases nutrients quickly, while slow decomposition creates a longer-term nutrient pool.
* **Root Systems:** Root systems vary from shallow, spreading roots in sawgrass to more extensive root systems in some SAV species. Root systems stabilize sediments and prevent erosion.
* **Resilience to Fire:** Many Everglades producers are adapted to fire, which is a natural part of the ecosystem. Sawgrass, for example, can quickly regenerate after a fire.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Everglades Producers
Everglades producers provide a multitude of benefits that are essential for the health and functioning of the ecosystem.
* **Primary Production:** They convert sunlight into energy, forming the base of the food web.
* **Habitat Provision:** They provide shelter, breeding grounds, and foraging areas for a wide range of animals.
* **Water Quality Improvement:** They filter water, remove pollutants, and oxygenate the water column.
* **Nutrient Cycling:** They facilitate the cycling of nutrients, making them available to other organisms.
* **Soil Stabilization:** They stabilize sediments and prevent erosion.
* **Carbon Sequestration:** They absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to mitigate climate change.
Users consistently report improved water quality and increased wildlife abundance in areas with healthy producer communities. Our analysis reveals that Everglades producers play a crucial role in maintaining the ecological integrity of the ecosystem.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are some frequently asked questions about Everglades producers:
1. **What are the biggest threats to Everglades producers?**
The biggest threats include nutrient pollution, altered water flow, invasive species, and climate change. Nutrient pollution can lead to algal blooms that shade out other producers, while altered water flow can disrupt natural cycles. Invasive species can outcompete native producers, and climate change can alter water levels and salinity.
2. **How does nutrient pollution affect periphyton?**
Excess nutrients, particularly phosphorus, can cause shifts in periphyton community composition, favoring certain algal species over others. This can lead to a decline in the overall quality and function of periphyton.
3. **What role does fire play in the Everglades ecosystem?**
Fire is a natural part of the Everglades ecosystem and helps to maintain its health. It removes accumulated dead vegetation, releases nutrients, and stimulates the growth of new vegetation. Many Everglades producers are adapted to fire and can quickly regenerate after a burn.
4. **How does altered water flow impact Everglades producers?**
Altered water flow can disrupt natural cycles of flooding and drying, which are essential for the health of many Everglades producers. Changes in water depth and duration can affect the distribution and abundance of different species.
5. **What can be done to protect Everglades producers?**
Protecting Everglades producers requires a multi-faceted approach, including reducing nutrient pollution, restoring natural water flow, controlling invasive species, and mitigating climate change. This requires collaboration among government agencies, scientists, and the public.
6. **Are all types of algae beneficial to the Everglades?**
No, some types of algae, particularly harmful algal blooms (HABs), can be detrimental to the Everglades. HABs can shade out other producers, deplete oxygen levels, and release toxins that harm aquatic life.
7. **How does salinity affect Everglades producers?**
Salinity can have a significant impact on Everglades producers, particularly in coastal areas. Some producers are more tolerant of salinity than others, and changes in salinity can alter community composition.
8. **What is the role of Everglades producers in carbon sequestration?**
Everglades producers play a crucial role in carbon sequestration by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during photosynthesis. This helps to mitigate climate change by reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
9. **How does the loss of Everglades producers affect the rest of the ecosystem?**
The loss of Everglades producers can have cascading effects throughout the ecosystem. It can lead to a decline in the abundance of herbivores, which in turn affects the abundance of carnivores. It can also disrupt nutrient cycling and water quality.
10. **What are some indicators of a healthy Everglades producer community?**
Indicators of a healthy Everglades producer community include a diverse range of species, abundant periphyton, clear water, and stable nutrient levels. Monitoring these indicators can help to assess the health of the ecosystem and identify potential problems.
Conclusion: Protecting the Foundation of the Everglades
Everglades producers are the cornerstone of this unique and vital ecosystem. Their ability to convert sunlight into energy sustains the entire food web, providing food, habitat, and essential ecosystem services. Understanding the roles of different producers, the challenges they face, and the actions needed to protect them is crucial for ensuring the long-term health and resilience of the Everglades. As we’ve explored, factors like nutrient pollution, altered water flows, and invasive species pose significant threats, but with informed action and collaborative efforts, we can safeguard these essential organisms. By supporting conservation initiatives and advocating for responsible water management, we can help ensure that the Everglades continues to thrive for generations to come. Share your experiences with Everglades producers in the comments below and explore our advanced guide to Everglades conservation for more in-depth information.
